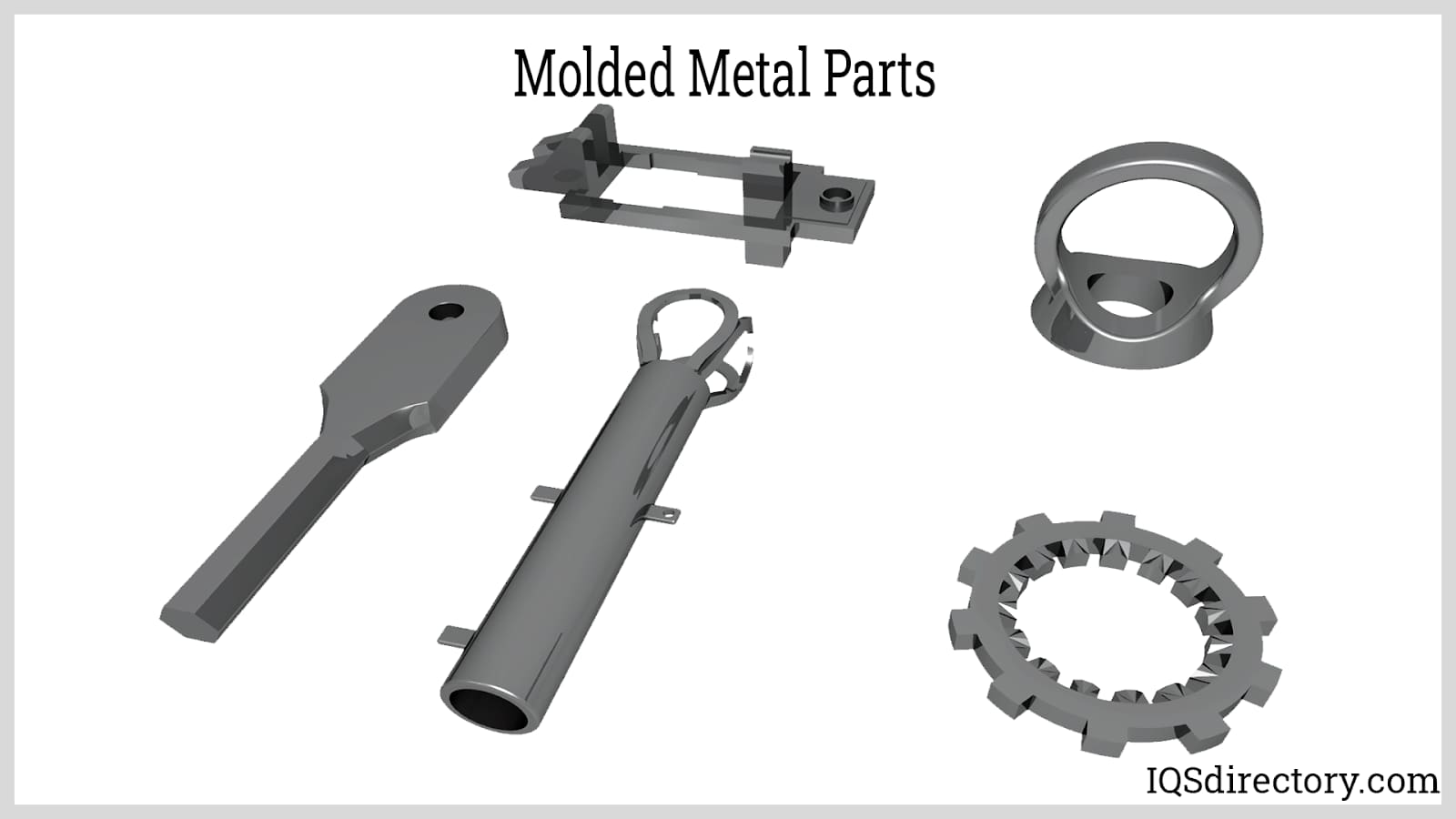
Metal injection molding (MIM) is a manufacturing process for fabricating small and precise metal components using finely-powdered metal, blended with a binder (binding agent), then solidified. Read More…
Since 1967, PSP has been a leader in small, intricate custom powdered metal parts for a wide range of industries, such as Sports & Recreation, Power Tools, Industrial Equipment, Oil & Gas.
Liberty Pressed Metals is a designer and producer of Powder Metals (PM) components for use in various industries, such as automotive, lawn and garden, office equipment, power tool, home appliances, and more. Our process boost product strength, precision, and durability. We are ISO 9001: 2015 certified. Our quality management system assures top-quality sourcing of materials, as well as unmatched...

Metaltech, Inc. has been in the metal powdered industry since 1989 in the heart of Dubois, Pennsylvania known as the capital of powdered metal. Our mission is too work with our customers to determine the efficient and economical method of production. We want to bring you the best product at the best price. Call today or visit our website for more information!

Our metal injection molding cannot be topped! We have years of field industry experience that we want to put to work for you. It is our mission that we will be able to offer high quality customer service as well as products that will withstand the tests of time to provide lasting value. For more information on what we may be able to do for you, get in touch with our customer service department...
Our design team develops and tests specific materials that are best suited for the intended application. By carefully reviewing various performance data, we can determine the most suitable material characteristics that will provide optimum performance during the product's life cycle. Our design group reviews our customers' existing processes and components, and in many cases, can design a powder...

Connor Corporation is a leading manufacturer of powdered metal parts. We offer a wide range of metals including non-ferrous metals, stainless steel, steel alloys, and specialty blend alloys. Bring us your customs designs and our team will work with you to fill all of your needs. Connor Corporation also offers various secondary operations including plating and finishing operations, all of which...
Founded in 1947, Clarion Sintered Metals is a trusted source for powdered metal parts. Clarion’s powder metallurgy specialists assist in the manufacturing of a variety of precision, cost-effective parts and components to ensure you receive the best in quality. From design assistance to finished sintered metal parts, ISO/TS 16949: 2002 registered Clarion has the expertise to meet any challenge.
More Metal Injection Molding Manufacturers
The metal injection molding cycle starts with the creation of the feedstock (the raw materials used to produce another material or item) by combining a binder made up of lubricants, polymers, waxes, and surfactants with a smooth metallic powder. The final feedstock is then ground into granules. Next, the feedstock is heated using an injection molding machine before being injected under pressure into a mold cavity. Time is then allowed for the molten feedstock to cool and solidify. A portion of the feedstock becomes a very porous brown substance once the binder components are eliminated. This brown component is subsequently sintered into more solid material and normally achieves over 95% of the density of the rest of the material, with no pores.
Metal Injection Molding Considerations
Metal injection molding can process almost any metal manufactured in an appropriate powder form. The adhering oxide film constantly presents on the surface of aluminum metal makes it an exception, as it prevents the sintering stage of the metal injection molding process. Numerous popular and less-common metals and their alloys are included in the list of metals that have been utilized in the metal injection molding process. The various metals processed through MIM include high-speed steels, superalloys, magnetic alloys, stainless steels, cemented carbides (hard metals), magnetic alloys, and intermetallic alloys.
Several factors make the choice of the binding particle used significant, including a powder’s density, the amount of metal contained in the feedstock, etc. Another surprising factor in selecting a binder is the shape of its particles. Typically, a spherical or nearly-spherical shape is preferable for MIM processes, although this also increases the chance of the skeleton deforming during the debonding stage. Coating each particle’s surface with a binder is another major factor to consider during the mixing process.
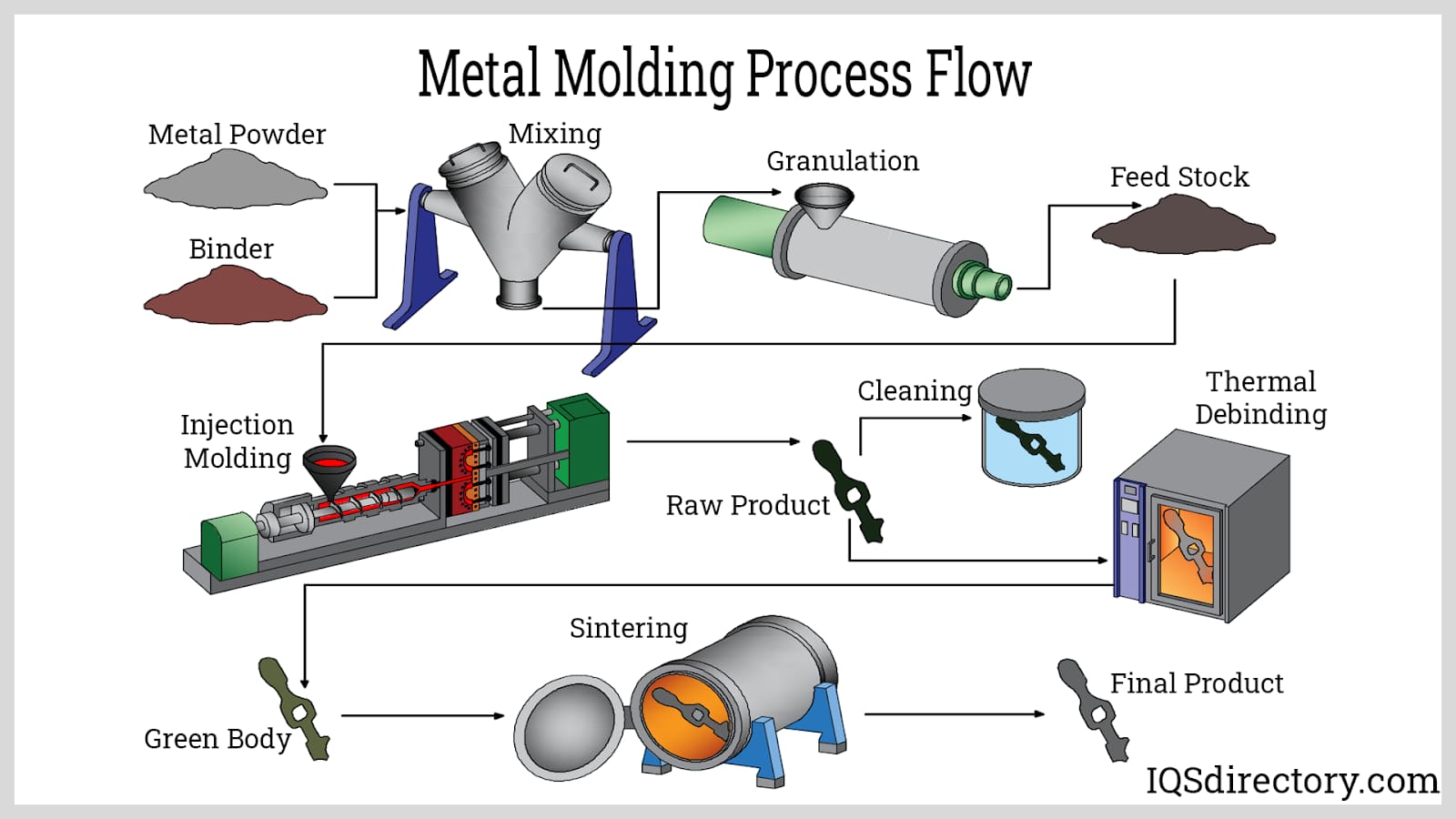
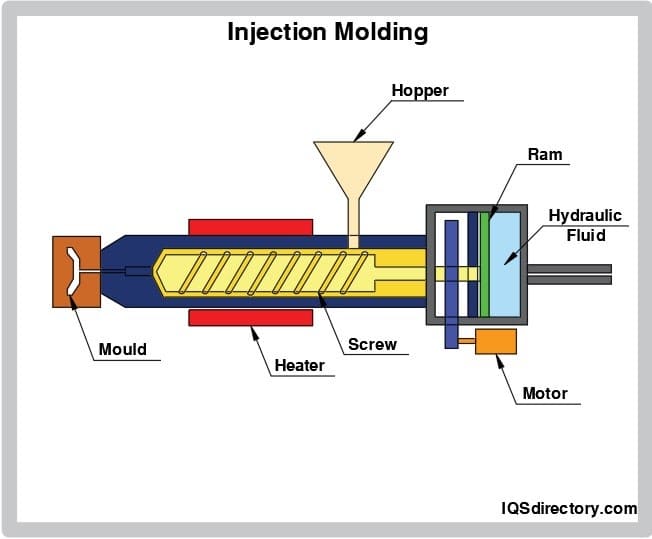
The feedstock mix is converted into solid pellets through a process known as granulation during the molding stage. To fabricate the best products, the temperatures of various metal injection machine components, including the nozzle used to inject the feedstock mix into the die and the screw which extrudes the mix through the die cavity, must be carefully maintained. The temperature of the die itself must also be managed, and it needs to be kept low enough to guarantee that removed components are set and solid.
Debinding, which involves removing the binding agent from the mold, is another crucial factor in metal injection molding, requiring extremely precise management. Two different processes are typically involved during debonding. In the first process, heat is applied to the mold and other equipment components to disintegrate any remaining feedstock material found on them. The second debinding procedure, which is only applicable to specific binder systems, involves dissolving the binder agent using suitable solvents like trichloroethane; again, heating is typically needed as the last step to complete the elimination of the binder material and solvent by evaporation.
Sintering creates a solid mass of material by applying pressure and heat to it without melting it to the point of liquefaction. Sintering is what provides a final product its strength. The procedure is done at temperatures usually below the metal’s melting point in controlled-environment furnaces in a vacuum and is crucial to prevent oxidation of the metal. The specific atmosphere of the sintering furnace depends on the metal type. For many metals, a simple atmosphere of hydrogen is sufficient. Still, for steel, where carbon serves as a crucial alloy ingredient, the atmosphere must contain one or more carbon compounds to maintain equilibrium with the steel, not to change this material’s properties.
Advantages of Metal Injection Molding
- Large production runs of metal components with intricate geometries and features are supported by metal injection molding. It works well for the high-volume production of small, precise parts with exact tolerances.
- Metal injection molding can precisely manufacture features, including internal and external threads, undercuts, holes, markings, and slots, without the need for additional machining or fabrication steps.
- Few limitations are placed on an item’s design through MIM. This process allows the opportunity to produce a wide range of shapes.
- Metal injection molding provides a smooth surface that can be improved through polishing.
- Metal injection molding can produce multiple parts from a single material piece.
- A variety of materials can be used in metal injection molding.
Disadvantages of Metal Injection Molding
- Metal injection molding can be pricey for modest production requirements.
- MIM may not be the best method for creating challenging metal fabrications.
- Metal injection molding is appropriate for small and medium-sized parts. Large part shaping, however, can reduce the mold’s ability to function properly and the furnace’s capacity, increasing process costs.
Choosing the Proper Metal Injection Molding Company
To make sure you have the most productive outcome when selecting a metal injection molding company, it is important to compare at least 4 companies using our metal injection molding directory. Each metal injection molding company has a business profile page that highlights their areas of experience and capabilities and a contact form to directly communicate with the company for more information or request a quote. Review each metal injection molding company website using our patented website previewer to get an idea of what each company specializes in, and then use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple metal injection molding companies with the same message.







 Cold Headed Parts
Cold Headed Parts Expanded Metals
Expanded Metals Metal Spinning
Metal Spinning Powdered Metal Parts
Powdered Metal Parts Roll Forming
Roll Forming Springs
Springs Wire Forms
Wire Forms Wire Mesh
Wire Mesh Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services